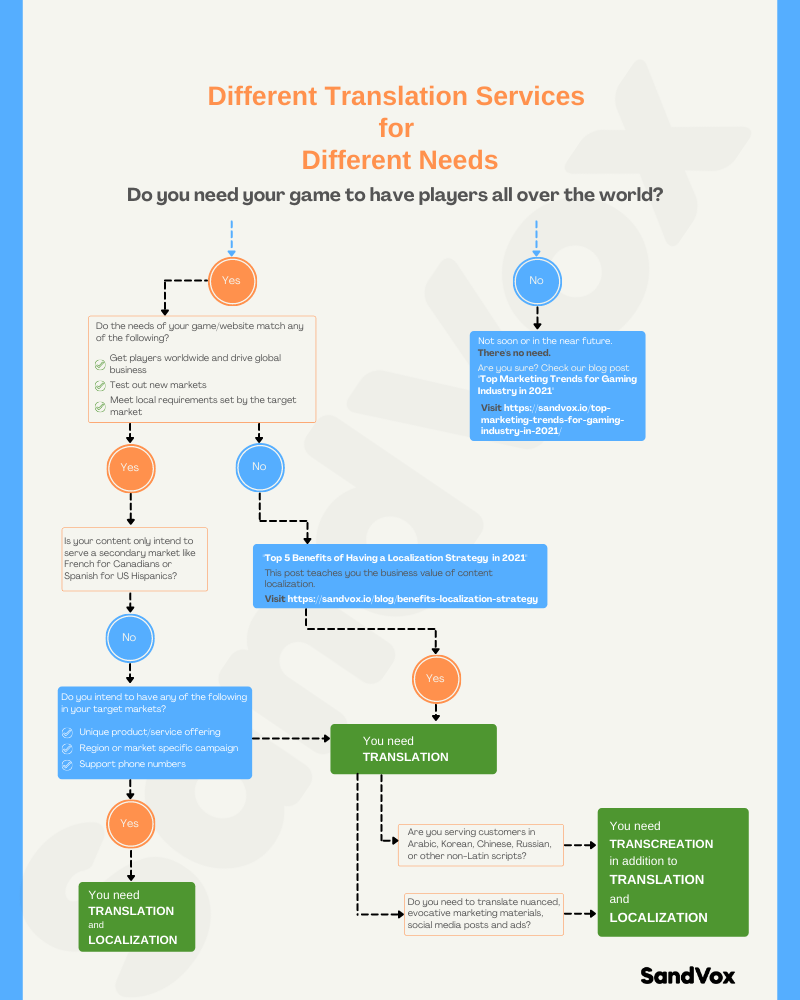
Translation, localization, or transcreation? Which language service is the best option for your communication needs?
Whether you are an established brand at the global level or are just planning to expand on the international market tempting to reach new customers, you need to create that engaging content that appeals to your audience. As a marketer or communicator, you need to know who your audience is, which are its characteristics, and what resonates the best with your prospects.
But how do make your branded content attract, engage and convert an international audience into paying customers? Because for sure a Japanese audience will digest your content in a completely different way than your American or French potential customers. A campaign that is very successful in a country or a region can sound occurred and offensive somewhere else.
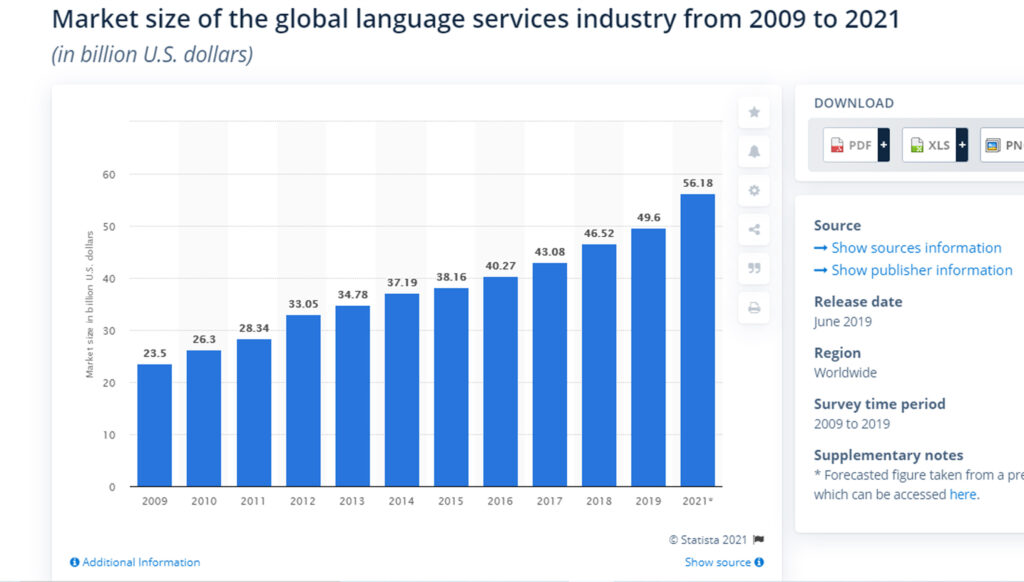
Well, the answer is not hard to find as due to translation services you will be able to convey your message in the right way to any audience worldwide. In fact, as the world is becoming increasingly interconnected, the market for the translation and localization industry reached 49.6 billion US dollars in 2019, double that ten years earlier.
Generally speaking, translation is the process of converting content from one language into another, replacing word-for-word. Pretty simple, easy, and straightforward, right?
Well…. Not quite. This definition tells just a part of the story. Because of all the processes involved, translation is somewhere at the border between science and art. Depending on your target audience, industry, budget, and business goals or communication channel, translation word-by-word might not be exactly the best approach. You would need to move forward with additional services, such as localization and transcreation.
But what exactly do they mean and how can help each service to convey the right message to your potential customers? Let’s break down these terms and find out why they are significant for your marketing activities.
Translation
While the process is simple, a literal translation often does not capture the cultural or locale-specific nuances of the target audience. Translators make sure to adapt the content into the new language so that it can be easy to understand by the local customers without injecting any creativity. The translation must keep the meaning of the original text by using different words and phrases where translation word-by-word is not possible.
Translation implies replacing words in the source–language with the equivalent words in another language. It involves keeping the content essentially the same. The content will reflect the signification of the original text and provide the same meaning to the readers in the translated language.
For instance, localization considers the format of dates, times, and currency. It considers whether users read from left-to-right (Western culture) or right-to-left (certain Middle Eastern and East Asian cultures). Images, graphics, and colors must also be adapted as they may convey different messages in different contexts. For example, white in European and American cultures represents the symbol of purity and innocence. On the other side, in Chinese culture, it also symbolizes purity and innocence, but white is associated with death and is a color commonly worn at funerals, too.
Localization
What is the localization and how can it help you when writing for a global audience? In its pure meaning, localization is part of translation, but making a step forward and sometimes, it can be a standalone service. Besides translating the words, localization takes into consideration the specific locale. In other words, this means you need to better understand the cultural, political, and legal standards of your target foreign audience and make sure your content doesn’t offend in any way their culture, values, and norms.
In many cases, certain words or expressions can be accepted in one region but stunned by another; or some specific colors or symbols might represent something good in the original context and something offensive to the receiving reader.
Localization, therefore, means taking into consideration all the local elements and adapting the original content in a way that is suitable to the local market.
Transcreation
While localization considers the specific locale, transcreation goes one step further. It implies the normal translation process but adds an additional creative twist. It takes the original message and adapts new wording, phrases, and images to make it relatable to the target audience. Transcreation takes a message and recreates it in a way that aims to get the same emotional response as the original.
Transcreation allows plenty of freedom of changing when adapting to a new audience. The goal is to restyle a message while maintaining the same emotions as the original text.
As the name suggests, it’s a blend between “translation” and “creation”. For example, the SandVox team is made of native linguists who are not just translators but also copywriters with great creative thinking. They will translate your original content and infuse it with their own creativity and local cultural knowledge while promising to keep the existing tone of voice, the intent of your content, and style. This way your project will be translated to meet a specific audience’s needs and get the same reactions and emotions as the original one.
When to Use Translation, Localization, and Transcreation
When is it appropriate to use each of these three techniques? The answer to this question depends strongly on your goals. Below we’ll list a few examples of which situations would be most suitable for each of the techniques:
Translation: All three methods utilize translation to some degree. However, a word-for-word or literal translation should only be used for simple content pieces. In translation, images, formats, and layouts all will typically remain the same – only the language changes.
Types of content that need translation:
- Technical documents
- Product files
- Legal documents
- Manuals
- Medical documents
Localization: This option is preferred when you want to convey the meaning to a different audience in a culturally relevant way. Therefore, your target audience will be more receptive as the text, formatting, and images are all adapted to their locale.
Types of content that need localization:
- Website content
- Apps and platforms
- Video Games
- E-Learning materials
- Graphic images, icons, and ads
- Any other kind of advertising document
Transcreation: The key element that is not found in either translation or localization is emotion. Transcreation is ideal when you want to fully adapt and connect with your new market. Content like film or artistic media – content meant to evoke emotion – might be good candidates for transcreation.
Other types of content that need transcreation:
- Sales and marketing collateral
- Advertisement texts
- Stories
- Video Games
- E-Learning documents
- Website content
- Blogposts.
Solution
SandVox is a premium one-stop-shop translation and localization agency addressing the gaming industry. Our team of expert translators and project managers put quality first and promise to produce great content that speaks to people from different cultures and boosts your game in particular and business, in general, all over the world.
If you’re planning to translate and match your content to people from the multilingual public, get in touch today and we’ll help you to get the service that best suits your needs.